Human Cells
Welcome to The Chat Afrika.com
Useful Articles
Chakra and it's applications | (By ChaosNature)
The Metaphysics of Human Experience | (By ChaosNature)
Human Cells | (By ChaosNature)
The Topic of Homosexuality | (By ChaosNature)
Floride and it’s effect in the Pineal Gland | (By ChaosNature)
What are cells?
What are receptors cell?
What is a gland?
What is an Organ?
What is a Neuron?
What is a central nervouse system and it’s function?
What are Hormones and what are their functions?
What is frequency?
These are the questions that I will be paying much attention to in order to clarify the relationship between information transmitted in the form of frequency to the physical cells that comprises the human anatomy.
“These chakras, or energy centers, function as pumps or valves, regulating the flow of energy through our energy system. The functioning of the chakras reflects decisions we make concerning how we choose to respond to conditions in our life. We open and close these valves when we decide what to think, and what to feel, and through which perceptual filter we choose to experience the world around us.” Ref ….
A cell as the name suggest is a compartment where molecules and elements are housed they are receptives in nature hence they act as recptors of light or more more precisely as receptors of informations these informations are transported along the blood stream in the formd that of what we call hormones , now the gland is a collection of specific receptor cells with similar genetic coding and forming eg the thyrod gland as different genetical arrangement from the pituitary gland the organs on the other hand is the combination of cells to carry out specific function
The relationship between the cell the glands , and the organs
When we think or send out a form of frequency through to the pineal glands the hypothalamus which comprises of specicial cells relates the information to the pituitary gland the information we receive into the human body system does not only come from the frequency emanated by our conscious or subconciouse thinking but also from the food that we ingest the codings withing the food communicates it’s codings or more precisely it’s information into our outer body cells refered to as the soma cells
The pineal (pronounced: pih-nee-ul) body, also called the pineal gland, is located in the middle of the brain. It secretes a hormone called melatonin
What Does the Endocrine System Do?
Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells
The hypothalamus is part of the brain. It maintains homeostasis (constant internal conditions) by regulating the internal environment (examples: heart rate, body temperature, water balance, and the secretions of the pituitary gland).
Gland
A gland is a group of cells that produces and secretes, or gives off, chemicals. A gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body. Some types of glands release their secretions in specific areas. For instance, exocrine (pronounced: ek-suh-krin) glands, such as the sweat and salivary glands, release secretions in the skin or inside of the mouth. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body
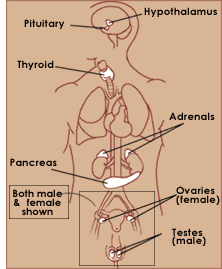
The major glands that make up the human endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pineal body, and the reproductive glands, which include the ovaries and testes.
hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (pronounced: hi-po-tha-luh-mus), a collection of specialized cells that is located in the lower central part of the brain, is the primary link between the endocrine and nervous systems. Nerve cells in the hypothalamus control the pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary.
Pituitary
Although it is no bigger than a pea, the pituitary (pronounced: puh-too-uh-ter-ee) gland, located at the base of the brain just beneath the hypothalamus, is considered the most important part of the endocrine system. It's often called the "master gland" because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands. The production and secretion of pituitary hormones can be influenced by factors such as emotions and seasonal changes. To accomplish this, the hypothalamus relays information sensed by the brain (such as environmental temperature, light exposure patterns, and feelings) to the pituitary.
Neurons
Neurons come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but they all have basically the same functional regions. Signals from other neurons or sensory cells are received on the dendrites and cell body (soma) and cause localized changes in membrane polarization. The electrical changes spread across the cell body and are combined at the axon hillock, located at the base of the axon. This is the region responsible for generating action potentials, which then travel quickly along the axon and its branches to the terminal knobs - small swollen areas at the end of the axon branches. Here the neuron interfaces with other cells at junctions called synapses through which signals are transmitted. Neurons that bring signals to the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) are referred to as sensory neurons, whereas those that carry signals from the central nervous system to the rest of the body are called motor neurons. Within the central nervous system there are also small, highly branched interneurons that help neurons communicate with one another. The axons of some vertebrate neurons have a fatty myelin sheath formed by supporting Schwann cells. This sheath helps support the fine axon and also increases the conduction velocity of nerve impulses (action potentials).
Melatonin
Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland, a pea-sized entity located near the base of the brain. The pineal gland helps regulate the hypothalamus gland and influences the functioning of the thyroid, thymus, pancreas and adrenal glands. Melatonin is produced from the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Melatonin has many functions, including working as an antioxidant and helping to regulate circadian rhythms (the body's biological clock which regulates the sleep-wake cycles). It also has a positive influence on the immune system, and it may act as a prophylaxis against osteoporosis, as well as an effective adjunct in the fight against certain types of cancers.
The metabolic pathway by which melatonin is produced
What Is the Endocrine System?
”The foundations of the endocrine system are the hormones and glands. As the body's chemical messengers, hormones (pronounced: hor-moanz) transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to another. Although many different hormones circulate throughout the bloodstream, each one affects only the cells that are genetically programmed to receive and respond to its message. Hormone levels can be influenced by factors such as stress, infection, and changes in the balance of fluid and minerals in blood.”
Organs
Organs use up frequency or energy that draw down from the glands that are related to them in the form of hormones , different forms of hormones stream through the blood at the same time and the glands which are the receptor cells receive their various frequency modulation that are designed specifically for their edification, these frequencies or information is then inturn tranfered or tramited to the organs , the viberational frequency that the result from the information gotten from the glands create the programming nessesary for the formation of behaviourism which is the by-product of the initial thought that was originally transmited from the being. The cells and it’s information determines the level of shophistication and intelligence of the body
What is Photosynthesis?
All organisms require energy for their chemical reactions. These reactions may be involved with reproduction, growth, or other activities. Photosynthetic organisms such as plants use light energy to produce carbohydrate (glucose). Glucose can be used at a later time to supply the energy needs of the cell. Photosynthesis is therefore a process in which the energy in sunlight is stored in the bonds of glucose for later use.
I sea a similarity to the formation of cells in plants and vergitable
Useful Articles
Chakra and it's applications | (By ChaosNature)
The Metaphysics of Human Experience | (By ChaosNature)
Human Cells | (By ChaosNature)
The Topic of Homosexuality | (By ChaosNature)
Floride and it’s effect in the Pineal Gland | (By ChaosNature)